Oracle Collaborative Planning
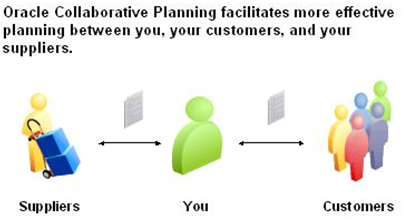
Oracle Collaborative Planning provides advanced capabilities for communicating, planning, and optimizing supply and demand information for trading partners across the supply chain. Oracle Collaborative Planning enables you to reduce inventory levels, improve visibility across your supply chain, increase the speed of information and materials, and promise delivery more accurately.
The following image depicts how Oracle Collaborative Planning works between you, your customers and your suppliers:
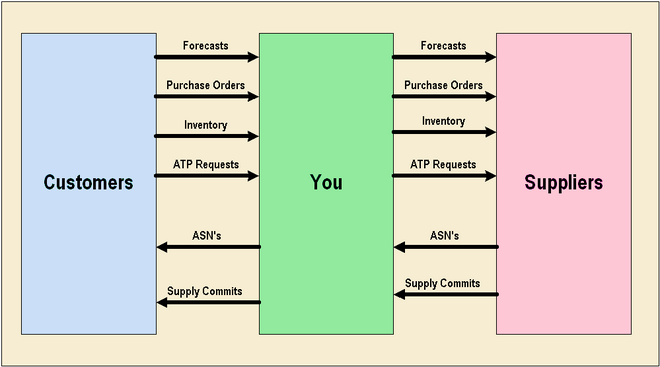
Oracle Collaborative Planning integrates with Oracle Advanced Supply Chain Planning, Oracle Demand Planning, and Oracle iSupplier Portal for a complete supply chain solution. You also can integrate Oracle Collaborative Planning with legacy ERP systems or use it as a standalone product.
Through integration, Oracle Collaborative Planning enables you to:
- Use data collections to acquire setup data from ERP legacy systems (items, customers, suppliers, users, company associations)
- Use data collections to access execution data, such as purchase orders and sales orders
- Publish order forecasts from Oracle Advanced Supply Chain Planning to your suppliers in Oracle Collaborative Planning
- Receive supply commits from Oracle Collaborative Planning to Oracle Advanced Supply Chain Planning
- Publish sales forecasts from Oracle Demand Planning to your customers in Oracle Collaborative Planning
Collaboration Methods
You can send and receive information into Oracle Collaborative Planning using the publish programs from Oracle Advanced Supply Chain Planning and Oracle Demand Planning, direct entry through the user interface, flat file loads, or XML.
You can publish order forecasts and supply commits from Advanced Supply Chain Planning to Collaborative Planning using MPS, MPP, MRP, and DRP plan types.
Basics of Collaboration
Collaborate with Customers

There are two types of collaboration business processes:
• Sales forecast collaboration
• Order forecast collaboration
Sales forecast collaboration is prevalent in the consumer goods industries, where promotions by both retailers and manufacturers have direct impact on end-consumer demand.
Order forecast collaboration is more common in manufacturing environments. Customers provide demand forecasts, and suppliers provide supply commit information based on their ability to meet the demand. Oracle Collaborative Planning enables your customers to publish forecasts in Oracle Collaborative Planning. You can then provide accurate supply commits based on those forecasts.
Collaborate with Suppliers

Collaboration with suppliers is similar to that with customers. With supplier collaboration, however, you are in the customer role and the supplier takes on your role. You must provide your suppliers with enough visibility to enable them to be more responsive to your requirements, reduce material shortages, view constraints early, and track performance. Two types of information collaborations are available:
- Sales forecast
- Order forecast
To prescribe the replenishment quantity to your suppliers, you can adopt any one of the following methods:
Min-max method: This method enables you to specify a minimum and maximum inventory quantity to be maintained at your own inventory organization.
Reorder point-fixed order quantity method: This method enables you to order a specific quantity whenever inventory drops below a certain minimum level.
Days of supply method: This method enables you to maintain inventory within the bounds of minimum and maximum days of supply. That is, you can specify the reorder point and reorder quantity in terms of days. When you publish an order forecast, the Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI) replenishment engine calculates and recommends a reorder quantity that translates this time horizon into days of supply.
Multi-tier Collaborations
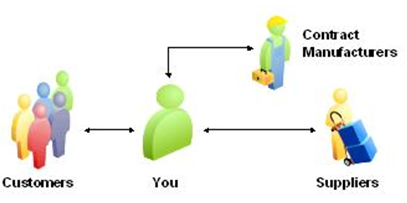
Oracle Collaborative Planning enables you to model any level of complexity in your supply chain and promote a seamless flow of information and materials across your extended supply chain. This enables you to provide visibility of your requirements to all tiers of your supply chain so that you can have visibility of all issues and constraints
in your supply chain.
Multi-tier collaborations enable you to:
- Communicate requirements to contract manufacturers and suppliers
- Get visibility to supplier capacity and customer requirements
- Reallocate key components
- Make alternate sourcing decisions
Oracle iSupplier Portal
When Oracle iSupplier Portal and Oracle Collaborative Planning are licensed, they can be combined in a unified portal (if they are deployed together in the same database instance). This provides your suppliers with one point of entry for planning and execution data.
The unified portal of Oracle Collaborative Planning and Oracle iSupplier Portal provides you with several capabilities. The following table lists those capabilities, and which application provides them.
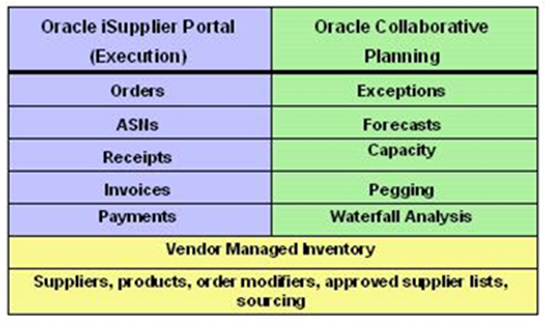
The suppliers can respond to purchase orders and initiate purchase order change requests directly through the Oracle iSupplier Portal. When this happens, Oracle Collaborative Planning auto-creates (for the purposes of supply/demand tracking and exception management within Oracle Collaborative Planning) a supplier sales order containing the acknowledgement information.
Suppliers can provide their sales order reference information directly through Oracle iSupplier Portal. This not only reduces overhead of maintaining documents in two separate places, but also enables a more streamlined business process.
Setup
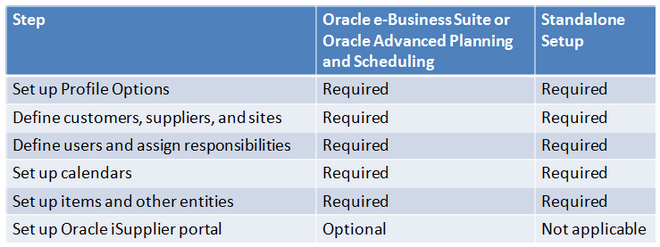
Implementation of Oracle Collaborative Planning depends on the application(s) its integrated with. Depending on the system, if any, you integrate Oracle Collaborative Planning with, you load data using different methods. Consider whether the following apply to your implementation:
- Implementation with Oracle e-Business Suite
- Implementation with Oracle Advanced Planning and Scheduling
- Implementation with Legacy systems
- Standalone setu
Notes: After completing the user, responsibility and other setups, Planning ODS Load and Data collection program should be run.
Deployment Configurations
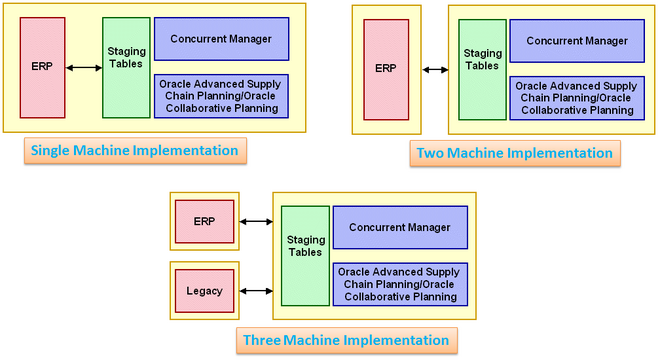
Begin your setup process by deciding on your deployment hardware configuration.
Oracle Collaborative Planning supports one, two and three machine implementations. These different deployment configurations enable planning calculations to be performed on different machines than the machine that performs transactions. This results in better system response.
The following are types of deployment configurations:
- Single Machine Implementation.
- Two Machine Implementation.
- Three Machine Implementation.
Users and Assign Responsibilities
Define Customers, Suppliers, and Sites
Create customers, suppliers, and in the source instance, then collect them to Oracle Collaborative Planning. After you set up your information in an Oracle ERP system, the data is collected into Oracle Advanced Supply Chain Planning and Oracle Collaborative Planning.
Define Customers and Customer Sites
Customers are defined in Oracle Order Management, using the Customers - Standard window. When defining a customer, enter the customer site in the location column. After defining your customers, run a targeted trading partners data collection to collect new customers into Oracle Collaborative Planning.
Define Suppliers and Supplier Sites
Suppliers are defined in Oracle Purchasing using the Supply Base - Suppliers window. When defining a supplier, enter the supplier site in the location column. After defining your suppliers and their sites, run a targeted trading partners data collection to collect new suppliers into Oracle Collaborative Planning.
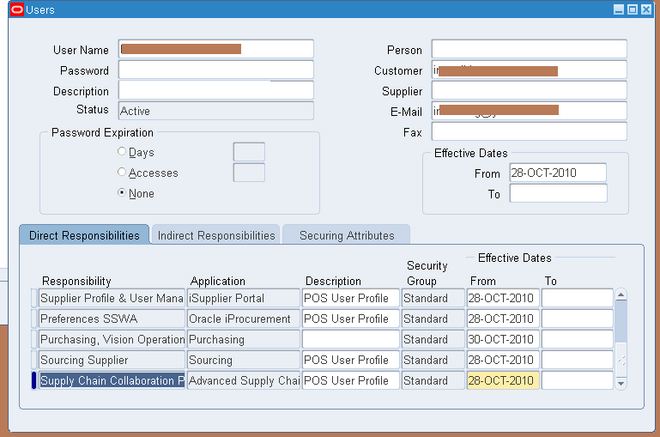
Define Users
You can define users that belong to your company, your supplier's company, or your customer's company. You must set up supplier users as contacts for supplier sites before they can be registered as users. Customer users must be setup as contacts for customer sites before they can be registered as users. After establishing the users in the
Oracle ERP system, run a targeted user company association data collection to collect new users. Select the option to create and enable user company association.
Oracle Collaborative Planning links the contact supplier information to the new user.
If your implementation of Oracle Collaborative Planning exists on a separate machine from the Oracle ERP system, then customer or supplier users must be established in the Oracle Collaborative Planning system.
To establish a customer or supplier user in Oracle Collaborative Planning, you must complete the following steps:
1. Define a new user by navigating to Security > User > Define. The System Administrator creates new accounts.
2. In the Users window, enter the same username you created in the Oracle ERP system and assign the Supply Chain Collaboration Planner responsibility.
3. Run a targeted data collection to collect company user association from the Oracle ERP system into the Oracle Collaborative Planning system. Set the flag on the Company User Association parameter to enable user company
association.
4. Maintain the company site information in the Oracle ERP system and collect data to Oracle Collaborative Planning.
5. Customers and suppliers can post their supplies and demands into the Oracle Collaborative Planning system.
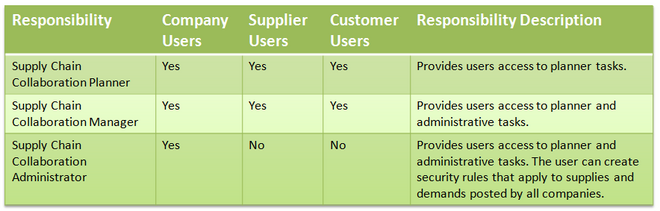
Assign Responsibilities
Reserve the Supply Chain Collaboration Administrator responsibility for a system administrator who has responsibility for the whole deployment. The following table lists the different types of users, which responsibilities you can assign to them, and the responsibility description:
Set Up Calendar
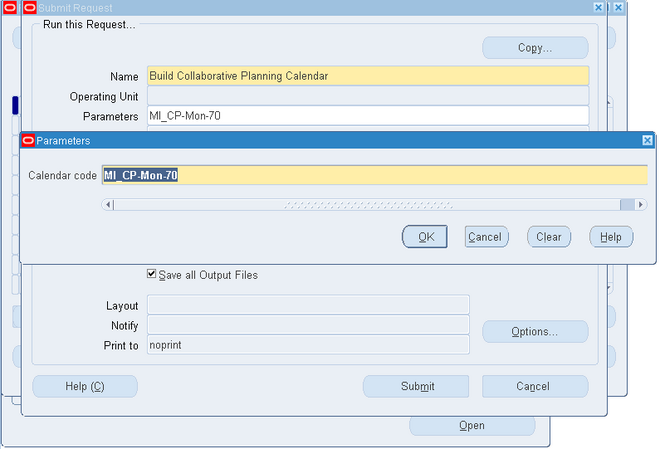
The calendar in Oracle Collaborative Planning is a 7-0 calendar, where all days are workdays, the week begins on Monday, and the month begins on the first day of the calendar month. Set up the calendar for Oracle Collaborative Planning by running the concurrent program Build Collaborative Planning Calendar.
Exceptions
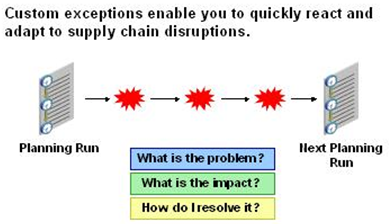
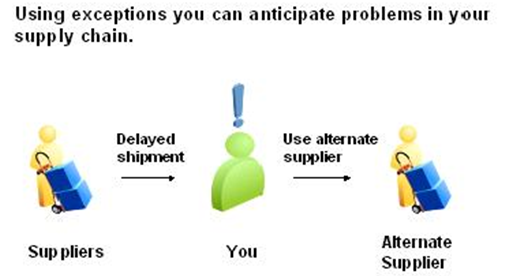
Exceptions are notifications that identify issues that need resolution. Oracle Collaborative Planning generates an exception whenever an actual process does not match the required process. For example, if you and your supplier's forecasts do not match, Oracle Collaborative Planning generates a forecast mismatch exception.
Exceptions ensure that the decision-making process remains focused, occurs in a timely manner, and makes the supply chain more responsive.
Oracle Collaborative Planning exceptions are grouped into several categories that correspond to supply chain problems. The categories are:
- Late orders
- Early orders
- Potential late orders
- Material shortage
- Material excess
- Forecast mismatch
- Response required
- Change orders
- Forecast accuracy
- Performance below target
Exception notifications for an item are sent to the supply chain collaboration planner for the item. If no planner is specified for an item, notification is sent to an Administrator. Any planner can view an exception through the Exceptions tab. You can also view counts for a given exception type.
Supply Chain Event Management Engine
The Supply Chain Event Management engine computes exceptions on a net change basis. Exceptions are computed only for every transaction that has received additional information since the last Supply Chain Event Management Engine run.
The Supply Chain Event Management Engine is a background process which usually runs at a specified frequency. Your Advanced Planning administrator can change this frequency.
View Exceptions
Complete the following steps to view exceptions in Oracle Collaborative Planning:
1. From the Oracle Collaborative Planning application, select the Exceptions tab.
2. On the Exceptions Summary page, select the exception type you want to view and then select Show Details.
3. You will see the details of the selected exceptions. You can perform a search on this page.
Seeded Exceptions
Collaborative Planning raises the exceptions related to shipping of materials from the supplier's site to the customer's site based on the key date on the purchase order issued by you or any of your trading partners. The key date is decided based on whether supplier or the customer is responsible for transporting the materials.
- If the supplier is responsible for transportation: Collaborative Planning considers the arrival (receipt date) date as a key date.
- If the customer is responsible for transportation: Collaborative Planning considers the ship date as a key date.
The following are the seeded exception categories for Collaborative Planning:
Late Orders
Late order exceptions occur when either you or your supplier are late in meeting a required date for an order. For example, if the Need By Date of a purchase order is 07/12/2003 and the system date is 07/22/2003, a late order exception is generated. The following late order exceptions are generated in Oracle Collaborative Planning:
Late Replenishment to Customer
• You see this exception as the supplier of an item.
• This exception is triggered when the receipt date on your sales order is later than the receipt date on the customer's purchase order and the threshold.
Late Replenishment from Supplier
• You see this exception as the customer of an item.
• This exception is triggered when the receipt date on the supplier's sales order is later than the receipt date on your purchase order and the threshold.
• By selecting this exception, you can navigate to the details of the purchase order that caused the exception (and related sales orders from the suppliers).
Replenishment to Customer is Past Due
• You see this exception as the supplier of an item.
• This exception is triggered when the system date is later than the receipt date on the customer's purchase order adjusted by the threshold.
Replenishment From Supplier is Past Due
• You see this exception as the customer of an item.
• This exception is triggered when the system date is later than the receipt date on your purchase order and threshold.
• By selecting this exception, you can navigate to the details of the purchase orders that caused the exception.
The details you can view of the purchase orders or sales orders that caused the exception include number of days the order is late by, exception types, order types, order numbers, release numbers, line numbers, items, quantities, order schedule dates (receipt date for the sales order, receipt date for the purchase order), order creation dates, and threshold days.
Material Shortage
Material shortage exceptions are discrepancies between your initial demand or supply and the corresponding supply or demand from your trading partner. Collaborative Planning exception engine enables you to generate Material Shortage exceptions by combining data for a base model and its configured items. The system tracks sales orders, order forecasts, and supply commits for configured items at base model level for exception generation. When the user drills down from the Vertical View through a sales order, the system checks if the item used in the sales order is a standard item or a configured item. If it is a configured item, the system compares aggregate order forecasts, supply commits and sales orders at a base model level and generates an exception if needed.
The following Material Shortage exceptions are generated in Oracle Collaborative Planning:
Supply Commit is Less Than Customer Order Forecast
• You see this exception as the supplier of an item.
• This exception is generated when the order forecast of a customer is more than your supply commit, adjusted to the threshold. The threshold is defined as percentage of order forecast.
Supplier's Supply Commit is Less Than Order Forecast
• You see this exception as the customer of an item.
• This exception is generated when supplier's supply commit is less than your order forecast, adjusted to threshold. Threshold for this exception is defined as percentage of order forecast.
Short Supply for Customer Purchase Order
• You see this exception as the supplier of an item.
• This exception is triggered when the quantity on your sales order is less than the quantity on the customer's purchase order.
• By selecting this exception, you can navigate to the details of the sales orders that caused the exception (and related purchase orders).
Short Supply from Supplier for Purchase Order
• You see this exception as the customer of an item.
• This exception is triggered when the quantity on the supplier's sales order is less than the quantity on your purchase order.
• By selecting this exception, you can navigate to the details of the purchase orders that caused the exception (and related sales orders).
VMI Item Shortage at Customer Site, Replenishment Required
• You can see this exception as the supplier of a VMI item.
• This exception is generated only for items which are enabled for VMI in the Approved Supplier List (ASL).
• This exception is generated when the total quantity of on-hand, requisitions, purchase orders, ASN (in-transit), and receipts for the item is less than the minimum quantity set for it.
VMI Item Shortage at Your Site
• You can see this exception as the customer of a VMI item.
• This exception is generated for items those are marked as VMI in the ASL.
• This exception is generated when the total quantity of On hand, Requisitions, Purchase orders, ASN, Receipts is below the minimum quantity set for the item.
From all these exceptions, you can navigate to the underlying transaction records, and review details.
Custom Exceptions

To prevent disruptions in the supply chain you must monitor and identify problems, determine the severity of issues to recognize when action is required, determine the appropriate corrective action, and measure performance to ensure appropriate actions are being taken. Custom exceptions enable you to define conditions that identify potential problems in the supply chain, receive notifications as problems are identified, and control the sensitivity of conditions by associating exception thresholds.
Oracle Collaborative Planning enables you to create business-specific custom exceptions. You can only edit the exceptions you created. When an exception condition is met an exception is generated, and a notification alerts you to the problem.
For custom exception definition, data is represented by three different views such as Company view, Supplier view, and Customer view. Attributes from these views are identified by the corresponding prefixes.
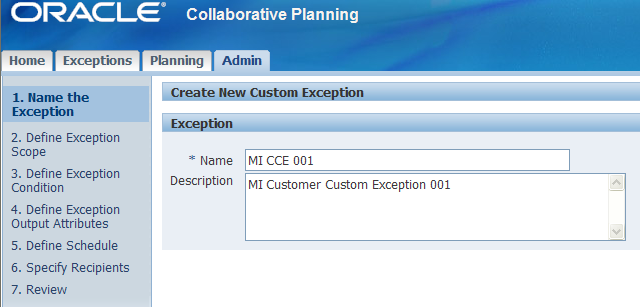
1. Name the Exception
Choose a name by which you will recognize and understand your exception. In this window you also can enter a description of your exception.
Define Exception Scope

You can limit the scope of a custom exception by entering filtering criteria. By limiting the scope, you are restricting the number of records to be evaluated for the exception condition. Setting proper scope helps improve performance of the exception generation process.
You can limit the scope of the exception by entering the following attributes and dates:
Limit Supply/Demand Attributes
• Company and/or Company Site
• Supplier and/or Supplier Site
• Customer and/or Customer Site
• Item and/or Owner Item
• Supplier Item and/or Customer Item
• Order Number
• Order Type Description
• Release Number
Limit Supply/Demand Dates
• Date Type
• Date Range
• Rolling Time Period
• Period to Date
While entering dates, you can use any of the date attributes present in the transaction by selecting suitable date type. You can define the range of dates as date range, rolling time period, or period to date which starts or ends on the current system date.
Define Exception Condition

This is the heart of the exception definition. Depending on the complexity of the exception definition, you can use Simple or Advanced conditions to model the exception condition.
Simple Condition
When defining an exception condition, verify that when the condition is true it results in an exception. Select whether to generate the exception when all the conditions are met, or when any of the conditions are met. Define the exception using the following criteria:
• Attribute
• Operator
• Value (from)
• Value (to)
While defining simple condition, you can also specify for this exception whether you want all the conditions required, or any of the conditions required. This is accomplished by selecting one of the following options:
• When all of the conditions are met
• When any of the conditions are met
Important: If there is no list of values available for a particular attribute used for the custom exception, the system shows a warning message. In such case, you should ignore this warning message and continue defining the condition.
Advanced Condition
If the Simple Condition window does not meet your exception definition, use the Advanced Condition definition window. In this window you use SQL to define conditions. In advanced condition, you can define conditions using attributes from three views such as Company, Customer, and Supplier.
Define Exception Output Attributes
Select the columns to display in your exception output by selecting attributes from the Available Attributes list. There are number of attributes available from all the three views. Carefully select the attributes required for your exception definition.

Define Schedule

You can schedule your custom exception to run independently or along with standard exceptions. If you decide to run the custom exception independently, then indicate when the system should start and how often it will evaluate the exception condition.
Enter the following information:
• Start Date
• Recurrence
If you decide to run it along with standard exceptions, it will be evaluated along with other seeded exceptions (with the frequency of Supply Chain Event Management engine).
Specify Recipients & Review

In this step, you can perform the following major tasks:
• Configure notification heading
• Specify workflow
• Specify recipient for the notification
Configure Notification Heading
In this step, you enter the text of the notification heading. You also can select from the output attributes by using tokens. For example, if one of your output attributes is Item Number, and you select this as token in notification header, the token will be substituted with the actual item number when the exception is generated.
Specify Workflow
By default, custom exceptions are governed by MSC:User Defined Workflow, and the User Defined Exception Workflow process. This workflow and workflow process generates the notification for each custom exception, and sends to the right users. You can customize this workflow, and workflow process, or add a new workflow process under the parent workflow, or add a new workflow to model your resolution procedure. If you have multiple workflows or workflow processes you can select the
most appropriate workflow for a particular exception in this screen.
Specify Recipients
Recipients can be specified as user, responsibility, item planner, or an e-mail address. For example, if you select recipient type as user, then the list of values for recipient will contain list of users in your instance. If you select item planner, the actual planner for the item will receive notification when the exception is generated.
You can enter whether to give access to the exception by enabling access to the Oracle Collaborative Planning exceptions window, by sending notification, or both by selecting appropriate check boxes.
Save
In the final step of custom exception creation you can review all of the setup data for your exception before saving it. After reviewing your exception and correcting any errors, select Submit.